Gluten Sensitivity Symptom Checker
How Are Your Symptoms?
Answer these 5 questions to get personalized guidance based on the article. Your responses will help determine if gluten might be causing your symptoms.
Your Assessment Results
When you stop eating gluten, your body doesn’t just switch off a food-it starts rewiring how it feels, digests, and even thinks. For some, the change is subtle. For others, it’s like flipping a light switch in a dark room. You wake up one morning and realize your bloating is gone, your brain isn’t foggy, and your skin isn’t breaking out. It’s not magic. It’s biology.
Your Gut Starts Healing
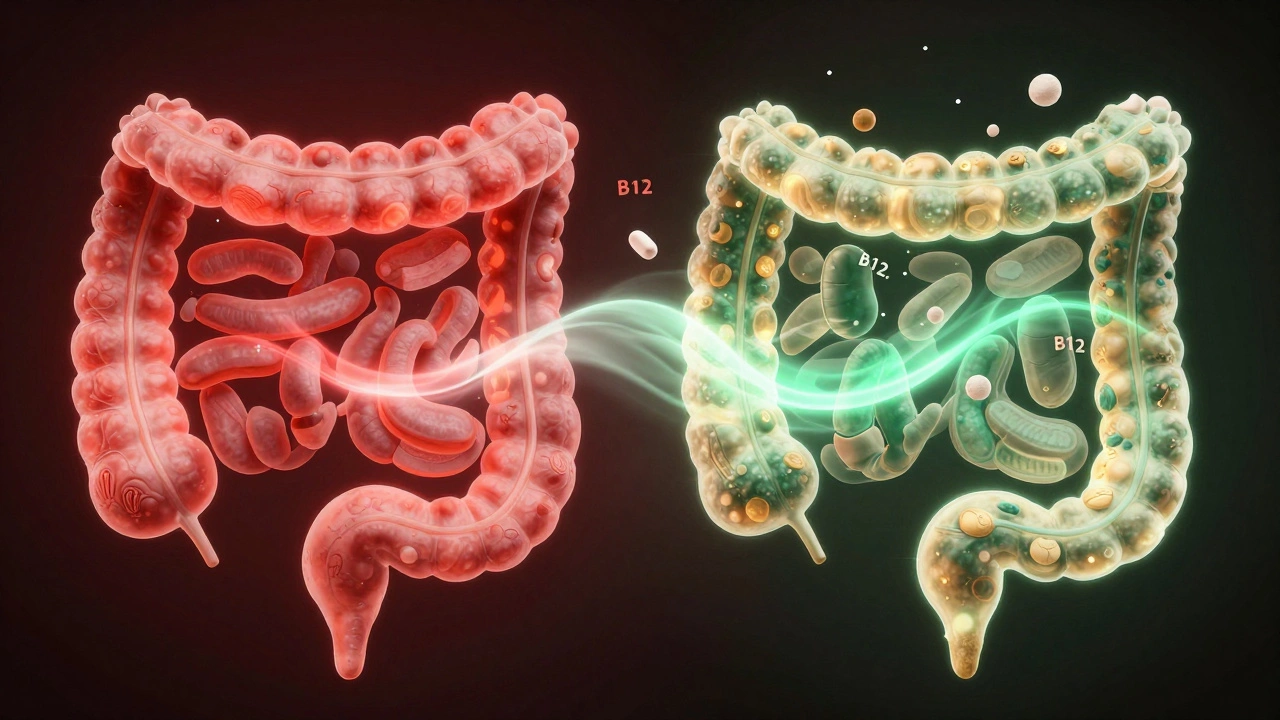
If you have celiac disease or non-celiac gluten sensitivity, gluten triggers an immune response that damages the lining of your small intestine. Those tiny finger-like projections called villi, which absorb nutrients, get flattened. When you remove gluten, your gut begins repairing itself. Within weeks, many people notice less bloating, fewer stomach cramps, and more regular bowel movements. A 2023 study in the Journal of Gastroenterology found that 82% of adults with gluten sensitivity reported significant improvement in digestive symptoms within 30 days of cutting out gluten.
This isn’t just about feeling better after a meal. It’s about your body finally absorbing the vitamins and minerals it’s been starving for. Iron, B12, calcium, and magnesium-nutrients often poorly absorbed in gluten-sensitive people-start to rebound. Fatigue lifts. Anemia improves. Bone density stabilizes.
Your Energy Levels Change
That constant afternoon slump? The need for three coffees just to get through the workday? For many, that’s not normal aging-it’s gluten. Gluten can cause inflammation in the gut, which sends signals to the brain that disrupt sleep, mood, and energy. When gluten is removed, inflammation drops. Blood sugar stabilizes. Your body stops wasting energy fighting something it shouldn’t be eating.
People often report feeling more alert within days. Not because of a caffeine boost, but because their brain isn’t fighting an invisible war. One woman in Wellington, who stopped gluten after years of chronic fatigue, said: "I didn’t realize I’d been living at 60% capacity until I turned it up to 100%."
Your Brain Gets Clearer
"Gluten brain fog" isn’t a myth. Studies show that gluten can affect the central nervous system in sensitive individuals. Headaches, trouble concentrating, memory lapses, even anxiety and depression-these can all improve when gluten is removed. A 2022 trial published in Neurology found that participants with gluten sensitivity who went gluten-free showed measurable improvements in cognitive function and mood within six weeks.
This isn’t about being "hyper-focused" like a productivity guru. It’s about the difference between struggling to remember where you put your keys and remembering without effort. Your thoughts feel less heavy. Decisions come easier. You stop rereading paragraphs because you lost track.
You Might Feel Worse Before You Feel Better
Here’s the twist: quitting gluten doesn’t always feel good right away. Some people experience withdrawal symptoms. Headaches, dizziness, nausea, irritability, even cravings. Why? Because gluten contains proteins that interact with opioid receptors in the brain. When you stop eating it, your body goes through a kind of detox. It’s temporary-usually lasts 3 to 7 days-but it’s real.
Don’t mistake this for failure. It’s a sign your body is adjusting. Drink water. Eat plenty of vegetables, eggs, lean meats, and fruits. Avoid replacing gluten with processed gluten-free junk food. That’s just swapping one problem for another.
Your Skin Might Clear Up
Chronic skin issues like eczema, psoriasis, or acne can be linked to gluten sensitivity. The inflammation triggered by gluten doesn’t stay in the gut-it travels. Skin is often one of the first places it shows up. Many people notice their rashes fade, their redness lessens, and their skin texture improves within a few weeks of going gluten-free.
One study tracked 120 people with persistent eczema who didn’t respond to creams or steroids. After 8 weeks of eliminating gluten, 71% saw major improvement. For some, it was the only thing that worked.
You’ll Start Eating Better-Even If You Didn’t Mean To
When you stop eating bread, pasta, crackers, and cookies made with wheat, you start looking for alternatives. You reach for vegetables, legumes, eggs, fish, nuts, seeds, and whole foods. You cook more. You read labels. You learn what’s really in your food.
You don’t need to buy expensive gluten-free bread. You don’t need to eat quinoa every day. You just need to eat real food. And that’s the biggest win. Your diet naturally becomes more diverse, more nutrient-dense, and less processed. That’s not a side effect-it’s the point.
Not Everyone Needs to Go Gluten-Free
Let’s be clear: if you don’t have celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, cutting out gluten won’t make you healthier. There’s no evidence it helps with weight loss, athletic performance, or longevity in people without a medical reason. Gluten isn’t evil. Wheat isn’t poison. For most people, it’s perfectly fine.
The problem isn’t gluten itself. It’s how much we eat-and how processed it is. A slice of sourdough made with ancient grains is worlds apart from a bag of industrial white bread loaded with additives. If you feel fine after eating pasta, keep eating it. Don’t follow trends. Listen to your body.

How to Know If You Should Try It
Ask yourself:
- Do you get bloated after eating bread or pasta?
- Do you feel foggy or tired after meals?
- Do you have unexplained skin rashes, joint pain, or headaches?
- Have you been told you have "IBS" but nothing helps?
If you answered yes to two or more, try cutting out gluten for 4 weeks. No cheating. No hidden gluten in sauces, soy sauce, or processed snacks. Then, slowly reintroduce it. Pay attention to how you feel. That’s the real test-not a blood test, not a trend, not a diet guru.
What to Eat Instead
You don’t need to live on rice cakes. Here’s what actually works:
- Vegetables and fruits
- Meat, fish, eggs
- Legumes: lentils, beans, chickpeas
- Nuts and seeds
- Gluten-free whole grains: quinoa, buckwheat, millet, amaranth, oats (certified gluten-free)
- Dairy (if you tolerate it)
Simple meals like grilled salmon with roasted sweet potatoes and broccoli, or a lentil stew with tomatoes and spinach, are naturally gluten-free and packed with nutrients. You don’t need fancy substitutes. You need real food.
What to Watch Out For
Gluten hides everywhere. Soy sauce, malt vinegar, salad dressings, spice blends, even some medications and supplements. Always check labels. Look for "certified gluten-free" on packaged foods. And be careful with cross-contamination-shared toasters, cutting boards, and fryers can ruin your progress.
Don’t fall for the trap of gluten-free junk food. Gluten-free cookies, chips, and cakes are still sugar, fat, and refined starches. They won’t heal your gut. They’ll just make you gain weight.
It’s Not a Diet. It’s a Reset.
Stopping gluten isn’t about losing weight or chasing a trend. It’s about removing something that’s causing harm to your body. For the right person, it’s life-changing. For others, it’s unnecessary. The key is to test it honestly-not because everyone else is doing it, but because you want to feel better.
If you try it and feel nothing? That’s okay. You learned something valuable. Your body doesn’t need to avoid gluten. And that’s just as important as finding out it does.
How long does it take to feel better after stopping gluten?
Most people notice improvements in digestion and energy within 2 to 4 weeks. Gut healing takes longer-up to 6 months for full recovery in celiac disease. Brain fog and skin issues often clear up faster, sometimes within days.
Can you develop gluten sensitivity later in life?
Yes. Gluten sensitivity and celiac disease can appear at any age. Stress, illness, surgery, or pregnancy can trigger it in people who previously had no issues. It’s not something you’re born with in every case-it can develop over time.
Is a gluten-free diet healthier for everyone?
No. For people without gluten sensitivity or celiac disease, cutting out gluten offers no proven health benefits. In fact, some gluten-free products are lower in fiber, iron, and B vitamins. A balanced diet with whole grains is better for most people.
What’s the difference between celiac disease and gluten sensitivity?
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder where gluten damages the small intestine and shows up in blood tests and biopsies. Gluten sensitivity causes similar symptoms but without the immune damage or positive test results. Both require avoiding gluten, but celiac is more serious and lifelong.
Can you eat oats on a gluten-free diet?
Yes-but only if they’re labeled certified gluten-free. Regular oats are often contaminated with wheat during growing or processing. Pure, uncontaminated oats are safe for most people with gluten sensitivity or celiac disease.





